Thursday, January 10, 2008
Made To Wear Sister's Girdle
I-MESOPOTAMIA
a-Creation and organization of the first cities. First inhabitants
The first villages and cities in the Middle East appeared on the banks of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, which form the Asian Mesopotamia. It was divided into two distinct zones
 Lower and Upper Mesopotamia
Lower and Upper Mesopotamia * Lower Mesopotamia: It was the most populated area and was near the mouth, where lower land fertile. He later received the Chaldean name. The first known inhabitants were the Sumerians, who were located in Lower Mesopotamia around 4000 BC. Since then the area was invaded successively by a lot of people who were changing the culture and lifestyle of the Mesopotamians.
* Upper Mesopotamia: This area is a mountainous and harsh plateaus. It was inhabited by the year 2300 BC by the Assyrian Semitic people, so that later was called Assyria. There, the Assyrians had to face the harsh and inhospitable rocky terrain which allowed only small livestock rearing. However, the Assyrian people did expanded to form a great empire.
The history of these peoples are known through Bible stories and scriptures engraved on clay tablets mainly.
b-The economy and social organization

Farming and ranching were the main economic activities. It grew wheat, barley, grapes, olives and date palms from which were extracted juices for beverages and textile fibers. Livestock farming was based on sheep and goats. Upon arrival of the Indo-Europeans was added horse breeding.
All economic activities were regulated. The exchange of goods and payment of taxes was made species. The value of the products was established by the king in metal. Trading activity was very active since controlled the maritime trade routes and land with the Far East.
metals came from Asia Minor, Lebanon timber and precious stones from India. From these materials brought from other countries, as Mesopotamia did not have these natural resources, developed crafts, metalwork, woodwork and metalwork.
 Details of the Code of Hammurabi laws
Details of the Code of Hammurabi laws
c-culture, science and religion. Culture
Cultures Mesopotamia were pioneers in many branches of knowledge, developed writing, at first pictographic and phonetic later, in the field of law, created the first codes of laws, in architecture, developed important advances such as the vault and dome .
His remains, though perhaps still a lot to learn, show a culture that exerted a powerful influence on other civilizations of the time and thus the development of Western culture. Religion
religions were polytheistic. In each city worshiped different gods, though some were common. Among these we can see: W: god of heaven, Enki: what is underneath, Nannar: Moon-god, Utu, the sun god, Inanna, goddess Venus, Polytheism: The doctrine that supports a plurality of gods, but in reality, most of the most seemingly polytheistic religions such as Greek or Hindu are monotheistic in which a Supreme Being manifests itself in various forms, as in the Hindu Trimurti whose main gods, Brahma, Vishnu and Shiva, are interrelated equivalent to those of the Christian Trinity. In such cases, historians of religions speak of a Deus Otioso, ie, a Supreme Being, for its sublimity, it is only accessible to the faithful through their manifestations or their angels intermediaries, or spirits. Generally, the same notion is found in so-called animist religions, which are discussed later. Something that was characterized and devalued their gods were related to arts that they were seeing for themselves gods also had livestock, writing, clothing, etc. This meant that they had a religion very broad and very interesting for someone it could be much more studied.

Sciences
The calculation flourished in Mesopotamia by a tenth and sexagesimal system, whose first application was in trade. Also known addition and subtraction multiplication and division and, after the second millennium BC, developed a mathematical equations could be resolved through third grade. Also knew the number π, the root and power, so they were able to calculate volumes and surfaces of the main shapes.
astronomical developments blossomed in the same way. The Sumerians knew the difference between moving objects-planets, and stars. But it was the Babylonians who further developed the field, being able to predict astronomical phenomena in advance. This knowledge of astronomy led them to adopt a precise lunar calendar, which included an additional month that fit the lot.
II-EGYPT
Egypt is the great civilization of the ancient world because that is what more or less stable will last from 3200 BC to the domination by the Roman Empire in the first century BC with Octavian Augustus. The coordinates of which are maintained despite the political and social changes throughout history.

In the course of the Nile is based the subsequent subdivision of the country in Upper Egypt (Thebes), Middle Egypt (Heptanomida) and Lower Egypt (Delta) with this division under the three major periods Historical: Memfita, Theban and Saite, including which are distributed thirty-three dynasties of pharaohs.
is this river that comes from distant regions, where rainfall is very heavy, the water that allows banks with their crops and life. This water sometimes overflows causing the periodic floods that force farmers to a long period of inactivity but sometimes insufficient, especially in distant lands of the river course. The losses in the marshy area and the lack of tributaries in this arid region may compromise the very existence of the river in the middle and lower very long journey, and the Nile would be exhausted through the thousands of miles of desert that stands before reaching the sea. The Nile River hydrographic regime is characterized by 2 annual floods that occur in summer so little regular, at least in its middle and lower. The river level begins to rise in June and reaches its peak in September, then declined gradually, reaching its lowest level between February and June.

STAGES OF EGYPTIAN HISTORY
 Upper Egypt is called the southern region, stretching from Memphis, near Cairo, to the first cataract, Asuán.Tenía an exceptional environment: comprised a very fertile plain by the floods of the Nile, and producing food surpluses. The cult of Horus was practiced all over Egipto.El supreme god of Upper Egypt was Seth and White crown symbol, the vulture goddess Nekhbet and white lotus flower, another symbol was the rush, which often present with Low Bee Egypt, preceding the cartridge containing the name of the pharaoh.
Upper Egypt is called the southern region, stretching from Memphis, near Cairo, to the first cataract, Asuán.Tenía an exceptional environment: comprised a very fertile plain by the floods of the Nile, and producing food surpluses. The cult of Horus was practiced all over Egipto.El supreme god of Upper Egypt was Seth and White crown symbol, the vulture goddess Nekhbet and white lotus flower, another symbol was the rush, which often present with Low Bee Egypt, preceding the cartridge containing the name of the pharaoh.
Middle Egypt (Heptanómida) It is not possible to determine at what period, if it really happened, the Heptanómida was considered a third territory of Ptolemy and Agatharchideslos Egipto.Según "Seven Nomos" were those of: Memphis, Heracleopolis; Cocodrilópolis, renamed Arsinoe; Afroditópolis, Oxyrhynchus; Cinopólis, and Hermopolis.
Lower Egypt was known in ancient Egypt to the north of the country, ranging from the Mediterranean to Memphis, near Cairo. Includes the whole Delta Nilo.Es "low" in relation to the course of the Nile was represented by the Red Crown and the bee. Asp also was the symbol of Lower Egypt and the vulture of Upper Egypt.
THE SOCIAL HIERARCHY

EGYPTIAN CULTURE AND EGYPTIAN ART EGYPTIAN ART
Big stones. Types of columns: Protodórica (simple abacus capital and stem of shallow grooves). The tombs. a mastaba. Burial chamber consisting of two parts. Mastabas important Karnak (temple of Karnak in Thebes), Luxor (Luxor Temple). Pyramid. IV dynasty. Temples. Interior columns providing ships. Parts of the temple: Avenue of the Sphinxes. Obelisks. Quadrangular prisms of great height. Pylons. Patio hipetro. Pillared hall. Room with columns and ceiling. Sanctuary. Closed room. Funerary temples. Dug into the rock. Known temple Abu Simbel. Hypogea.
 EGYPTIAN CULTURE
EGYPTIAN CULTURE
 constructions of the Egyptians were mostly of adobe, material created with mud and straw, due to the absence of stones and wood in the area. Only the great temples and stone burial structures used canteras.La taken from the Egyptian house was built around a patio.La house had a square with a central space preceded by an anteroom. All around we find the bedrooms and rooms for storage. This structure does not vary in relation to social class habitantes.Gruesas columns serve to anchor the structure of these cottages, tall, narrow door of which was raised above ground level. On the roof of the house stood the roof.
constructions of the Egyptians were mostly of adobe, material created with mud and straw, due to the absence of stones and wood in the area. Only the great temples and stone burial structures used canteras.La taken from the Egyptian house was built around a patio.La house had a square with a central space preceded by an anteroom. All around we find the bedrooms and rooms for storage. This structure does not vary in relation to social class habitantes.Gruesas columns serve to anchor the structure of these cottages, tall, narrow door of which was raised above ground level. On the roof of the house stood the roof.

The stool was the Egyptian cabinet as universal in its use are not social distinctions. More elitist is the chair and beds made of wood. The trousseau was linen and used a headrest for sleeping, some even stone.

III-THE PERSIAN EMPIRE

Old Middle Eastern country, which occupies the end of the twentieth century the territory of Iran, especially the Zagros Mountains, east of Mesopotamia.
Connoisseurs of all these historical records, infer with some confidence that the Persians were part of a family tribe, who were members of an even larger group designated by the name of Aryans, a diverse group of nomadic tribes whose original homeland lay probably in the Eurasian plains of southern Russia. Roughly between 2000 and 1800 BC, the Aryans began their migration by moving some to the Indian subcontinent, while others guided his steps to the west through Iran and penetrated to the northern part of Mesopotamia and Syria. Around 1400 BC, a third group of Aryans that would include the Persians moved inland from the northwest of Iran and gradually moving westward.

Gutis.
Elamite Empire.

Media.
Persian Empire.
UK Delivery.
Sassanid Empire.
Umayyad Caliphate. Abbasid Caliphate
.
Il-Khans.
Safavid Empire.
Iran.

Persia has been a term used extensively in the West to name the territory of modern Iranian province of Fars, and in its broadest sense, the entire area known as Iran increased. This term was first used by the Greek people because of their belief that Perses, son of the mythological Perseus, founder of Mycenae and Andromeda, princess of Ethiopia, would settle in the territory of Zagros Mountains, and its offspring the royal line of Persian emperors.
In the Achaemenid period, this myth would be used advantageously by Xerxes I to convince the city of Argos to fight on his side, insisting that both countries shared the same ancestor, because for the people of Argos he was Persian.
However, today we know that Persia is simply the name Hellenized Parser, which in ancient Persian means "above reproach."
After the Arab invasion of Persia, the Muslims, have no equivalent in the alphabet the letter "P", Fars call him, since this is its current name.
-Map of Ancient Near East.
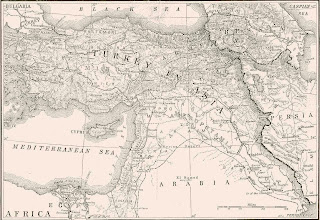 gold-Tablet with cuneiform writing. -Ziggurat
gold-Tablet with cuneiform writing. -Ziggurat  Khorsabak Palace.
Khorsabak Palace.  -Ishtar Gate.
-Ishtar Gate.  "The lioness wound.
"The lioness wound.  -Map of Pharaonic Egypt.
-Map of Pharaonic Egypt. 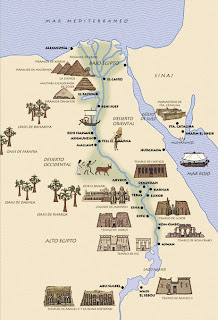 -hieroglyphic writing, hieratic, demotic.
-hieroglyphic writing, hieratic, demotic. 


egipcios.
-Gods-sketch of an Egyptian temple of Karnak
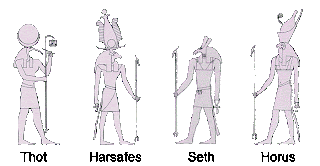 .- Sanctuary.
.- Sanctuary.  -Abu Simbel.
-Abu Simbel.  -Pyramids of Giza.
-Pyramids of Giza.  -Sphinx. Hypogeous
-Sphinx. Hypogeous  -Tomb of the Kings Valley.
-Tomb of the Kings Valley.  -Write sitting
-Write sitting  .- The Beled-el-Sheikh.
.- The Beled-el-Sheikh.  -Bust of Nefertiti.
-Bust of Nefertiti. 
0 comments:
Post a Comment