Arabia is a peninsula at the junction of Africa and Asia, between the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Aden and Red Sea. It is also known as the Arabian Peninsula.

Muhammad during his lifetime, Muhammad entrusted the preservation of the Word of God (Allah الله), transmitted by Gabriel (Jibreel, جبريل), the retention of memoriones, those who tirelessly reciting memorized. Muhammad did not reject completely the Jewish and Christian religions, but claimed to have been sent by God to complete and perfect their teachings. Then war broke out between Makkah and Yathrib, which Muhammad's followers were victorious. Later Muhammad's successors expanded the domain of Arab rule in Palestine, Syria, Mesopotamia, Persia, Egypt, North Africa and Spain.

Islam is the religion that was born of the teachings of Muhammad. The prophet taught that man must submit completely to the will of God. So Islam means "submit" and its devotees, Muslims, are "those who submit."
According to Islamic tradition, one night when Muhammad meditated on Mount Hira, the angel Gabriel appeared and told him the existence of one God (Allah) and that he, Mohammed, would be his prophet, so that its mission was spread the word of God to the infidels (unbelievers).
Since the attacks, on 16 July 622 the prophet and his followers migrated to Yathrib, that would be since the "city of the Prophet" (Madinat al-Nabi or Medina) and its center of operations. In this episode of his life, when Mohammed fled from Mecca and began his pilgrimage, called the Hijra and it marks the end of the pre-Islamic era and the beginning of the era of Islam, as Muslims consider year zero of the lunar calendar. Expansion
 islamica.Además, nomadic Bedouins assume a Pan-Arabian consciousness, thanks to Islam. The early conquests are a assertion of Arab political sovereignty in the area. The Islamic state offers political stability to the region and in principle a little Islamization of the structures of power. However, this is also the time when ending the Arab hegemony over the Islamic state. The Islamic state will disintegrate in multiple states fully feudal character, like the Christian kingdoms.
islamica.Además, nomadic Bedouins assume a Pan-Arabian consciousness, thanks to Islam. The early conquests are a assertion of Arab political sovereignty in the area. The Islamic state offers political stability to the region and in principle a little Islamization of the structures of power. However, this is also the time when ending the Arab hegemony over the Islamic state. The Islamic state will disintegrate in multiple states fully feudal character, like the Christian kingdoms. 
The first califas.Tras Muhammad, the Muslim community was ruled by consensus, although not without tension. The first Caliphs were all colleagues and even family of Muhammad. (Caliph or Khilafat Allah means God's representative)
Throughout history, many rulers and dynasties of caliphs took the title, but that greatly expanded the Islam were the first of them.
The perfect or orthodox caliphate, which lasted from 632 to 660, consisted of the first four successors of Muhammad that, from its capital at Medina, led the conquest of a territory that included much of North Africa, Mesopotamia, Syria and Persia.
The Umayyad Caliphate, 660 to 750, with its capital in Damascus held the gains from the Iberian Peninsula to India.
The Abbasid Caliphate moved the capital to Baghdad. Between 750 and 1258, the Abbasid dynasty tried to consolidate the gains, developing trade and effective management. However, from the ninth century their empire was fragmenting into several simultaneous Caliphate and suffered various invasions, such as the Mongols, who after converting to Islam got that from the thirteenth century, the Muslim religion from spreading all over India , albeit without converting the majority of the population. Especially in India is where the eastern boundary lies the majority of the expansion of Islam until today.  Rahman III 912 to 961
Rahman III 912 to 961
The caliphate is the last major Turkish from 1517 to 1919. The Turkish monarch took the title of caliphs from 1517, when Selim I conquered Mecca and Medina. Before they had defeated Byzantine Empire and Islam had succeeded in extending the center of Europe. In its heyday, the Turkish territory to Hungary came from Algeria, through Egypt, Arabia and Mesopotamia. The last Turkish Caliph was overthrown in 1919.
II.-political organization (the caliphate, Caliph, Koras, emir, vizier, Kadi), economic (agriculture and trade), social (the Medina, the Arabs, Muladi, the Mozarabic) and Muslim cultural.
political organization.
- Transformation patriarchal structure of a multinational empire.
- Implementation of an absolutist state dominated by Arabs.
- Khalifa, head of the community of believers.
- will be surrounded by a court of bureaucrats and officials.
- The capital of the empire was in Damascus (Syria), governed directly by the caliph.
- The rest of the provinces by governors with civil and military powers.
- Iraq, Khurasan and Transoxiana, Hijaz, Yemen, Egypt, Africa, Al-Andalus.
 Abd al-Rahman II becomes the fourth Umayyad emir in Cordoba after the death of his emirate released padre.Recién war breaks out in Cora de Tudmir between Yemeni clans and muraditas. Cora was established in the southeast peninsula and its capital was the present Orihuela.
Abd al-Rahman II becomes the fourth Umayyad emir in Cordoba after the death of his emirate released padre.Recién war breaks out in Cora de Tudmir between Yemeni clans and muraditas. Cora was established in the southeast peninsula and its capital was the present Orihuela.
Abd al-Rahman II founded Mursiya (current Murcia) between 825 and 831 in a small rise on the river Segura, in order to pacify the country, promote development and strengthen its authority.
In Muslim sources quoted General Hisano Unmayya ibm ibn Mu'awiya as peacemaker and Cora Todmir Chabar as first governor general of Murcia.
Abd al-Rahman II was willing to create a new capital for Tudmir Cora.
Rarely in history, except in America and the founding of Alexandria, has been the desire to create a capital, even if province, from the beginning of its existence.
 The word comes from the Arabic Amir Amir ʾ (أمير), which in turn is formed with the root word comes from Arabic amir (أمير). The sequencing, word in turn derived from the root ʾ AMR (أمر) command. Were the governors of each of the provinces.
The word comes from the Arabic Amir Amir ʾ (أمير), which in turn is formed with the root word comes from Arabic amir (أمير). The sequencing, word in turn derived from the root ʾ AMR (أمر) command. Were the governors of each of the provinces.  Vizier (Arabic, وزير Wazir) is in a historical context of Islam, a position equivalent to prime minister, used an assistant or monarch.
Vizier (Arabic, وزير Wazir) is in a historical context of Islam, a position equivalent to prime minister, used an assistant or monarch.  A kadi (Arabic قاضى) is a judge of the Muslim territories, which applies the sharia. Kadi word means to judge and shares meaning with Sheik, but differs in that the Sheik will judge could exercise a governor of the city.
A kadi (Arabic قاضى) is a judge of the Muslim territories, which applies the sharia. Kadi word means to judge and shares meaning with Sheik, but differs in that the Sheik will judge could exercise a governor of the city. 
Economics in traditional Muslim cities was governed by a corporate system that integrated the men engaged in the production, distribution and services, and act as owners or workers, home workers, self-employed or employees of government , whether "people of high or low status, Muslims, Christians and Jews, native or naturalized foreigners, all belonging to the enterprise system" (Yusuf Ibish 1976). Corporations in the urban population was grouped according to their offices, and that was to be craftsmen, merchants, auctioneers, pawnbrokers, musicians, singers, storytellers carriers and sailors.
The members of each corporation is considered both as members of the community of believers whose service was credited efficiency especially in the profession or occupation, which was acquired through hard work supervised by a teacher ("Shaykh") turn connected to the chain of teachers of the corporation, which was binding on the other, the patron saints and even to the Prophet.
Corporations are structured as a concept and ritual passed down orally from generation to generation and closely related the Sufi orders (Islamic lodges). Upon acceptance of a young apprentice in a workshop following the recitation of the first "sura" (chapter) of the Koran to the teachers of the corporation and a period of years of zero or low pay which was compensated by the idea that was that the means to learn and to integrate socially into the community.
 Medina (Arabic: مدينة madina). The word means "city." His full name is Madinat an-Nabi (Prophet's City), Madinat Rasul Allah (City of the Messenger of God) or Al-Madina al-Munawwara (City Light), because it arose the first Muslim community. Formerly called Yathrib. Most city dwellers accepted Muhammad as leader. In the vicinity of the city built the first mosque called Quba Mosque and the city and the house of Muhammad was the first major meeting place for Muslim prayer. A month later, the Muslims of Medina decided to march on Mecca.
Medina (Arabic: مدينة madina). The word means "city." His full name is Madinat an-Nabi (Prophet's City), Madinat Rasul Allah (City of the Messenger of God) or Al-Madina al-Munawwara (City Light), because it arose the first Muslim community. Formerly called Yathrib. Most city dwellers accepted Muhammad as leader. In the vicinity of the city built the first mosque called Quba Mosque and the city and the house of Muhammad was the first major meeting place for Muslim prayer. A month later, the Muslims of Medina decided to march on Mecca.
 is known as al-Andalus to the territory of the Iberian peninsula under Muslim rule during the Middle Ages (711-1492). Stages
is known as al-Andalus to the territory of the Iberian peninsula under Muslim rule during the Middle Ages (711-1492). Stages domain of Islam in al-Andalus 711-756
: emirate dependent on Damascus. Al-Andalus is governed by the Umayyads.
756-929: independent emirate of Baghdad. Members of the Abbasid dynasty Umayyad murder. Escapes Abd-al-Rahman I who takes refuge in Cordoba. 929-1031
: Caliphate of Cordoba, Abd-al-Rahman III proclaimed caliph.
1031-1261: Taifa Kingdoms. Political division of al-Andalus. Independent kingdoms called Taifa.
1238-1492: Kingdom of Granada. Last bastion of al-Andalus and the last independent kingdom of peninsular Muslim majority.
Conquest
The invasion and subsequent occupation of southern Spain was held by military. The presence of Muslim invaders north of the Central System is almost anecdotal, limited military incursions. Either way, the battle of Simancas disrupted plans to install Muslim Arab populations in the vicinity of the Duero and wilderness areas.
Caliphate of Cordoba
In 929, Abd al-Rahman III established the Caliphate of Cordoba, claiming religious independence from Baghdad, capital of the Abbasid Caliphate. The proclamation of the Caliphate contained a twofold purpose:
- Inside: the Umayyads wanted to strengthen its position.
This is the political phase of greatest splendor of the Umayyad state which is then transformed into various kingdoms called "Taifa Kingdoms.
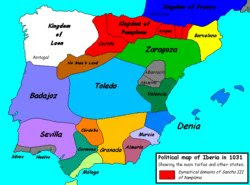 First
First Taifa Kingdoms
Each taifa identified at first with a family, clan or dynasty. Over the years, the Taifa of Seville (who had conquered all of western Andalusia and the eastern part), Badajoz, Toledo and Zaragoza, were the Islamic powers Peninsula.
Lacking the necessary troops, the Taifa hired mercenaries to fight their neighbors or to oppose the Christian kingdoms in the north. Even Christian warriors, like the Cid himself, served the Muslim kings, fighting even against other Christian kings. However, this was not enough and the Christian kingdoms would take the Muslim division and weakness of each individual to submit Taifa. Faced with this threat, the Taifa kings sought help from the Sultan of the North African Almoravids, Yusef Ben Tashfin, who passed the strait and not only defeated the Castilian king at the Battle of Zalaca (1086), but gradually conquered all Taifa.
Second and third
Taifa kingdoms
When Almoravid rule began to fall, arose the so-called second Taifa kingdoms (1144-1170), which were subsequently submitted by the Almoravids, who had succeeded the Almoravids in your domain North Africa.
After the end of the Almohad period, marked by the battle of Navas de Tolosa, was a short called "Taifa Kingdoms third, which ended with the founding of the Nazari kingdom of Granada, who did not capitulate until 2 January 1492, when it officially ends the Reconquista.
are asesinadosCuando The Umayyads of Damascus last Umayyad caliph was killed by the Abbasids there was a change in the ruling dynasty in Damascus. The new Abbasid dynasty ordered the murder of all the Umayyads who were in the empire.
The last Umayyad prince al-Andalus reached the last prince who survived was called Abd-al-Rahman. He escaped and reached al-Andalus, to become its new emir, with the name of Abd-al-Rahman I started a new period in Muslim history in the Iberian Peninsula.
Abd-al-Rahman I Abd-al-Rahman I was proclaimed emir (prince and military leader) and broke the link between al-Andalus and Damascus. Managed to bring peace between the various Muslim groups. With it began the independent emirate, which would be the year 756 to 929. Throughout these years, set a centralized state similar to its predecessors in the East, with a more stable management structure and a mercenary military force composed of Berbers in North Africa and bought slaves in southern Europe. SLIDE

: 1.-Plant
Mosque of Cordoba.

2.-Archery (bow) of the Mosque of Cordoba.

3.-Arco, dome and facade of the mihrab of the Mosque of Cordoba.

4 .- minaret of the mosque of Cordoba.

5.-Palacio de Medina Azahara in Cordoba.

6.-Oratory Aljafería of Zaragoza. Archways.

7.-Alcazaba of Malaga.

8.-La Giralda in Seville.

9.-The Torre del Oro in Seville.

10.-Santa Maria la Blanca in Toledo.

11.-Plan of the Alhambra.

12.-Salas and courtyards of the Alhambra: Mexuar Room, Patio of the Myrtles, Hall of Ambassadors, courtyard of the lions, the two sisters room, the viewpoint of Dajara, Gate of Justice.
13.-The Generalife.
0 comments:
Post a Comment