Fernando V of Castile and II of Aragon, also called the Catholic, was born on May 10, 1452 in Sos, Zaragoza. Son of John II of Aragon and Juana Enríquez, was proclaimed king of Sicily (1468), King of Aragon (1479-1516) and Castile (1474-1504).
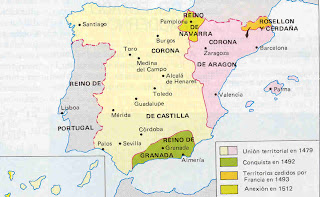
He married Isabella of Castile, which caused a civil war in Castile between supporters of Isabel and Juana la Beltraneja. Finished the race in 1479, Ferdinand and Isabella ruled jointly, "the Catholic Kings," who conquered the last Muslim stronghold on the Iberian Peninsula with the fall of Granada in 1492. Fernando
an actively collaborated with Isabel in all matters pertaining to Castile, as well as those of Aragon and foreign policy. Both worked together to unify their domains and encourage their development. In 1476 organized the Santa Hermandad, an institution that had its own militia dedicated to protecting the rural population of the bandits and keep order in the wilds. In 1480 created the Inquisition to impose religious unity and suppress any dissent. Http://www.cervantesvirtual.com/historia/monarquia/catolicos.shtml

territorial unification
startreign.
to reign in Castile, Isabel had to overcome the opposition of an important part of the Castilian nobility, especially the nobility, who preferred the alliance of Castile to Portugal, which sided with Jane, the Beltraneja, which ended in a clash of the battle armado.Tras Toro (1476), the court met in Madrigal de las Altas Torres proclaims Queen Elizabeth I. Conquest of Granada

Once
said Elizabeth on the throne of Castile, he resumed the conquest of the Nazarite kingdom of Granada. Taking advantage of the kingdom was in a dynastic crisis between the sultan, his brother and his son Boabdil Zagal, began the war for the conquest of Granada. Several phases are distinguished:
(1469): They marry the Catholic Monarchs.
(1484 to 1487): Conquest of the western part of the kingdom. Boabdil signed a treaty with the Kings, under which deliver Granada in return he was given an estate in the eastern part of the kingdom.
(1488 to 1490): Start the conquest of the east of the kingdom. He moved the base of operations to Murcia. During this stage yields Zagal.
(1490 to 1492): It requires the surrender of Granada Boabdil. Grenadian people to learn the terms of the agreement, resists, which is answered by the armies of the Kings. Boabdil final delivery to Granada after secret negotiations.
Victory in this war meant:
The appearance of an army structured and professional, regardless of the nobility, who would comprise the actual thirds.
The provision of economic resources.
The award and appeasement of certain sectors of the nobility by dividing the territories of Granada between them.

Incorporation of the Canary Islands
sovereignty of the Canary Islands to Castile was granted by the Treaty of Alcaçovas (1479), defining the English and Portuguese territories, but not be achieved fully submit to the islands until the conquest of Tenerife in 1496, the so-called Peace of Los Realejos.

The conquest of Navarre
Navarra was divided in the early sixteenth century into two camps: agramonteses and beamonteses, each favors a different king. In this confrontation, the kings of Navarra signed a treaty with the king of France that threatened to Spain. Because the kings of Navarra promoted certain religious doctrines that angered the Pope, issued a bull of excommunication against them.
In 1512 Ferdinand Navarra asked permission to natural ally of France (Understand this in the environment of ongoing rivalry between Aragon and France) - English troops to pass through Navarra to attack France. The negative response by the king of Navarre was enough Ferdinand to the Duke of Alba ordered the occupation of Navarra, and sending aid to his supporters, the beamonteses-and in less than a year, the English part of the Kingdom of Navarre (Upper Navarra) joined the Monarchy Catholic. Only be met with resistance in some parts of south and could tell that story Pamplona, \u200b\u200bthe capital, fell in only three days.

political institutions
Kingdom of Castile
the Royal Council was remodeled in the Cortes of Toledo in 1480, making it more structured and modular.
Hearing was formed Granada. There was an increase in the English Treasury due to taxes and estates division of the territory from the Nazarite.
to control banditry on the roads, and general theft, was instituted in 1476 the Holy Brotherhood (forerunner of today's Civil Guard), which would be the first state police in Europe. In the municipalities of the magistrates were established dominion, the pervasive authority at the municipal level.

Corona de Aragón
hardly changed. Most important was the greatest power given to the deputies in the area and the establishment of the electoral lottery, consisting out of a paper bag with the nominee. This innovation remained for 30 years, when the King dies, and this rule is forgotten.
religious policy
Pope Innocent VIII granted to the Catholic kings the right to Board on Granada and the Canary Islands, which meant the state control on religious matters.
A bull of Pope Sixtus IV in 1478 established the Inquisition in Castile to control the purity of the faith. Because Aragon was from 1248, so the English Inquisition was the only common institution for the two kingdoms. It was a hard stage as Fray Tomas de Torquemada Inquisitor General.
in 1492 expelled the Jews, of great economic power in Spain, producing an economic crisis. Left Spain about two thirds, becoming the other. Also forced Muslims to convert to Christianity Moorish-passing call or leave Spain.
The result of this act of religious cleansing was to create a country of Christian religion and the beginning of the identification of country and religion.
is establishing permanent Embassy of Spain to the papacy, which is the first permanent embassy in the world and the first time used the name of Spain for a settlement official.

Economy and Society
The expulsion of the Jews was a great economic loss to Spain.
Castilla was the industrial power and largest trading and Aragon the time was not far behind. The economic base was in industry, agriculture, sheep farming and the export of raw materials. To defend the wealth that wool meant the Kings granted privileges to the Mesta to the Law on Defence of the Canadas in 1489, threatened by farmers. Artisans were protected by the domestic trade. Social and economic
favored medium to high nobility, which had increased its economic power with the dominions of Granada. The Laws of Toro in 1505 strengthened the institution of primogeniture.
In Catalonia solved the problem of the farmers of remensa with the Sentence of Guadalupe (1486), which removed the bad habits and forced farmers to pay new taxes.

Foreign Policy
The aggressive and expansionist foreign policy carried out by Ferdinand and Isabella was made possible by a number of factors:
The diplomatic initiative of Ferdinand II of Aragon. Its purpose was to get the best deals for his kingdom. Continued policy Aragon traditional to the Mediterranean with an eye in the East, as evidenced by its flag (see below paragraph Blasones).
The efficiency of the army of the Crown under the command of Gonzalo Fernandez de Cordoba, known as the Great Captain. Fernández de Córdoba organized the army on a new combat unit, the third, or real-thirds, which involved the creation of the first modern army of the Crown, regardless of the retinues of nobles.
The great contribution of funds from industry and trade of wool and wheat.
matrimonial policy of kings.
inherit the title in 1502 Emperor and Autocrat of the Romans.
marriage policy of the Catholic Monarchs also included marriage alliances for their children. Were these:
Isabel, married to Prince Alfonso of Portugal, and after Manuel I of Portugal, a cousin of her first husband.
Juan, married Margaret of Austria and died prematurely (1497). He is buried in the monastery of Santo Tomás de Ávila.
Juana (Juana la Loca), married Philip of Austria (Philip the Handsome), son of Emperor Maximilian I of Austria.
Mary, married to Manuel of Portugal, his brother in law, the death of his sister Isabel.
Catherine, she married the Crown Prince of England, Arthur, and following the untimely death of the latter, with his brother, who later became Henry VIII of England.
In conclusion, it was aimed at seeking an alliance with Portugal and the creation of a coalition opposed to France which, although it had not been an enemy of Castile, had always argued claims to certain territories of the Crown of Aragon, to shew heir to the empire of Charlemagne.

The expansion in the Mediterranean: Italy
Charles VIII's army moved to Southern Italy, dethroning Alfonso II, King of Naples and a relative of Ferdinand. In 1500 the new king of France Louis XII King Ferdinand signed the Treaty of Granada to hold together the kingdom of Naples. Fernando agreed, and the King of Naples, Federico IV at the time, was dethroned. For the relief sought by the Pope, Fernando around Rome with his troops for a possible French attack to dismiss the Pope. Succession




 islamica.Además, nomadic Bedouins assume a Pan-Arabian consciousness, thanks to Islam. The early conquests are a assertion of Arab political sovereignty in the area. The Islamic state offers political stability to the region and in principle a little Islamization of the structures of power. However, this is also the time when ending the Arab hegemony over the Islamic state. The Islamic state will disintegrate in multiple states fully feudal character, like the Christian kingdoms.
islamica.Además, nomadic Bedouins assume a Pan-Arabian consciousness, thanks to Islam. The early conquests are a assertion of Arab political sovereignty in the area. The Islamic state offers political stability to the region and in principle a little Islamization of the structures of power. However, this is also the time when ending the Arab hegemony over the Islamic state. The Islamic state will disintegrate in multiple states fully feudal character, like the Christian kingdoms. 
 Rahman III 912 to 961
Rahman III 912 to 961  Abd al-Rahman II becomes the fourth Umayyad emir in Cordoba after the death of his emirate released padre.Recién war breaks out in Cora de Tudmir between Yemeni clans and muraditas. Cora was established in the southeast peninsula and its capital was the present Orihuela.
Abd al-Rahman II becomes the fourth Umayyad emir in Cordoba after the death of his emirate released padre.Recién war breaks out in Cora de Tudmir between Yemeni clans and muraditas. Cora was established in the southeast peninsula and its capital was the present Orihuela.  The word comes from the Arabic Amir Amir ʾ (أمير), which in turn is formed with the root word comes from Arabic amir (أمير). The sequencing, word in turn derived from the root ʾ AMR (أمر) command. Were the governors of each of the provinces.
The word comes from the Arabic Amir Amir ʾ (أمير), which in turn is formed with the root word comes from Arabic amir (أمير). The sequencing, word in turn derived from the root ʾ AMR (أمر) command. Were the governors of each of the provinces.  Vizier (Arabic, وزير Wazir) is in a historical context of Islam, a position equivalent to prime minister, used an assistant or monarch.
Vizier (Arabic, وزير Wazir) is in a historical context of Islam, a position equivalent to prime minister, used an assistant or monarch.  A kadi (Arabic قاضى) is a judge of the Muslim territories, which applies the sharia. Kadi word means to judge and shares meaning with Sheik, but differs in that the Sheik will judge could exercise a governor of the city.
A kadi (Arabic قاضى) is a judge of the Muslim territories, which applies the sharia. Kadi word means to judge and shares meaning with Sheik, but differs in that the Sheik will judge could exercise a governor of the city. 
 Medina (Arabic: مدينة madina). The word means "city." His full name is Madinat an-Nabi (Prophet's City), Madinat Rasul Allah (City of the Messenger of God) or Al-Madina al-Munawwara (City Light), because it arose the first Muslim community. Formerly called Yathrib. Most city dwellers accepted Muhammad as leader. In the vicinity of the city built the first mosque called Quba Mosque and the city and the house of Muhammad was the first major meeting place for Muslim prayer. A month later, the Muslims of Medina decided to march on Mecca.
Medina (Arabic: مدينة madina). The word means "city." His full name is Madinat an-Nabi (Prophet's City), Madinat Rasul Allah (City of the Messenger of God) or Al-Madina al-Munawwara (City Light), because it arose the first Muslim community. Formerly called Yathrib. Most city dwellers accepted Muhammad as leader. In the vicinity of the city built the first mosque called Quba Mosque and the city and the house of Muhammad was the first major meeting place for Muslim prayer. A month later, the Muslims of Medina decided to march on Mecca.  is known as al-Andalus to the territory of the Iberian peninsula under Muslim rule during the Middle Ages (711-1492). Stages
is known as al-Andalus to the territory of the Iberian peninsula under Muslim rule during the Middle Ages (711-1492). Stages 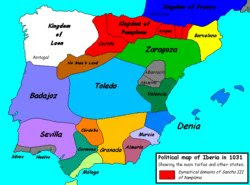

















 Lower and Upper Mesopotamia
Lower and Upper Mesopotamia 






 EGYPTIAN CULTURE
EGYPTIAN CULTURE  constructions of the Egyptians were mostly of adobe, material created with mud and straw, due to the absence of stones and wood in the area. Only the great temples and stone burial structures used canteras.La taken from the Egyptian house was built around a patio.La house had a square with a central space preceded by an anteroom. All around we find the bedrooms and rooms for storage. This structure does not vary in relation to social class habitantes.Gruesas columns serve to anchor the structure of these cottages, tall, narrow door of which was raised above ground level. On the roof of the house stood the roof.
constructions of the Egyptians were mostly of adobe, material created with mud and straw, due to the absence of stones and wood in the area. Only the great temples and stone burial structures used canteras.La taken from the Egyptian house was built around a patio.La house had a square with a central space preceded by an anteroom. All around we find the bedrooms and rooms for storage. This structure does not vary in relation to social class habitantes.Gruesas columns serve to anchor the structure of these cottages, tall, narrow door of which was raised above ground level. On the roof of the house stood the roof. 





 gold-Tablet with cuneiform writing. -Ziggurat
gold-Tablet with cuneiform writing. -Ziggurat  Khorsabak Palace.
Khorsabak Palace.  -Ishtar Gate.
-Ishtar Gate.  "The lioness wound.
"The lioness wound.  -Map of Pharaonic Egypt.
-Map of Pharaonic Egypt. 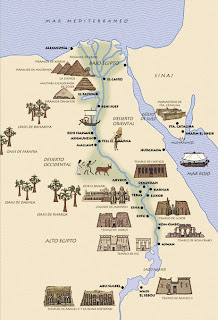 -hieroglyphic writing, hieratic, demotic.
-hieroglyphic writing, hieratic, demotic. 


 .- Sanctuary.
.- Sanctuary.  -Abu Simbel.
-Abu Simbel.  -Pyramids of Giza.
-Pyramids of Giza.  -Sphinx. Hypogeous
-Sphinx. Hypogeous  -Tomb of the Kings Valley.
-Tomb of the Kings Valley.  -Write sitting
-Write sitting  .- The Beled-el-Sheikh.
.- The Beled-el-Sheikh.  -Bust of Nefertiti.
-Bust of Nefertiti. 